Fluid management and administration of blood products should be guided by the trauma team leader along with paediatric team. The use of inotropes is not uncommon and should be started when hypotension exists inspite of adequate fluid/ blood replacement. Please prepare inotropes according to the monograph.
Intraosseus route
Intraosseous (IO) route is frequently used in emergency resuscitation of paediatric patients. Please follow the local guidance for different brands and types of intraosseous needles.
Indications:
- Intravenous fluids or medications are urgently needed and a peripheral IV cannot be established after two attempts or 90 seconds and the patient exhibits one or more of the following:
- An altered mental status (GCS of 8 or less)
- Respiratory compromise (SaO2 90% after appropriate oxygen therapy, respiratory rate < 10 / > 40 min)
- Haemodynamic instability (systolic BP less than age accepted normal).
- IO should be considered PRIOR to peripheral IV access attempts in the following situations:
- Cardiac arrest (medical or traumatic)
- Profound hypovolemia with alteration of mental status
- Patient in extremis with immediate need for delivery of medications and or fluids.
Contraindications:
- Fracture of the bone selected for IO insertion (consider alternate site).
- Excessive soft tissue at the insertion site with the absence of palpable anatomical landmarks (consider alternate site).
- Previous significant procedures (IO within 24 hours – consider alternate site).
- Infection at the site selected for insertion (consider alternate site).
Procedure:
- If patient is conscious informed verbal consent should be obtained.
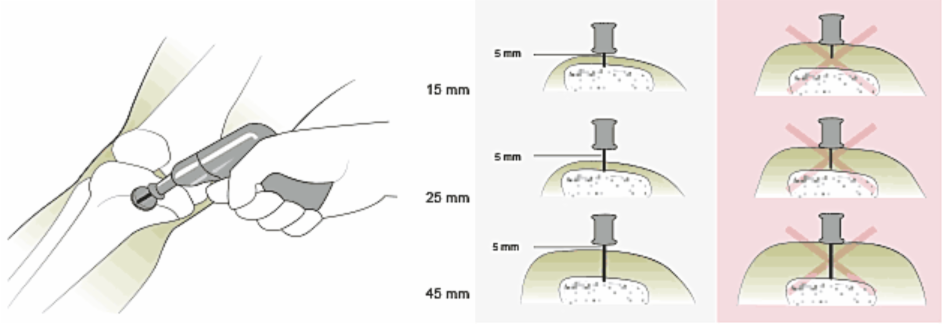
- Use age appropriate needle (EZ-IO, the most commonly used intraosseous needle in the region comes in three sizes)
- EZ-IO PD® 15mm (3–39 kg)
- EZ-IO AD® 25mm (40 kg and over)
- EZ-IO AD® 45mm (excessive tissue).
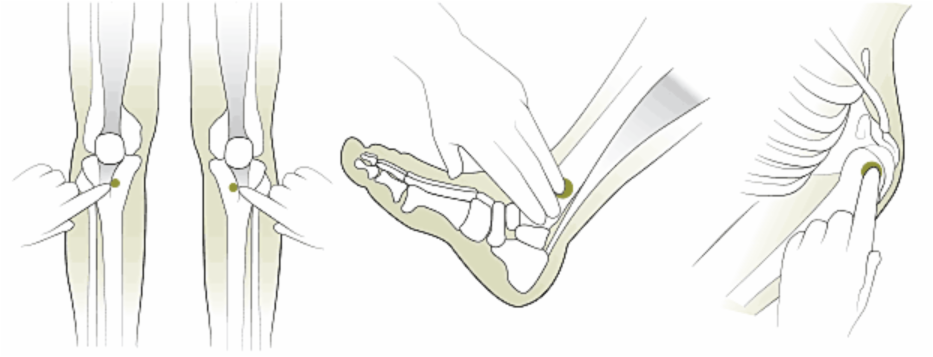
- Locate appropriate insertion site
- aseptic technique
- Stabilise site (this may need additional help from second person)
- Position driver at 90 degree angle to the insertion site as shown in figure. Gently power or press needle set down until needle touches the bone.
- Penetrate the bony cortex by squeezing the driver’s trigger and applying gentle steady downward pressure.
- Release the driver’s trigger and stop insertion process when sudden ‘give’ or ‘pop’ felt or desired depth is achieved.
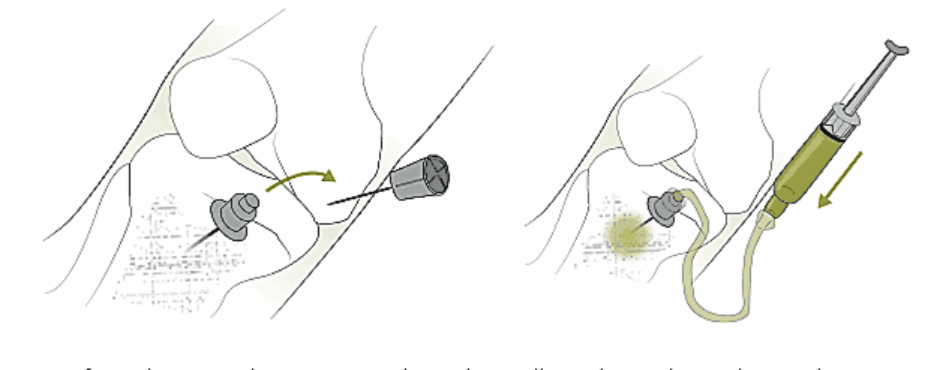
- Remove power driver and stylet.
- Confirm placement by aspirating through needle and sample can be used for analysis.
- Consider slow administration of 1– 2 ml of 2% lignocaine through the EZ-IO prior to starting infusion as bolus infusion can cause severe discomfort.
- Flush the catheter with 10 ml syringe bolus of saline. NO FLUSH = NO FLOW
- Start infusion under pressure (syringe bolus, infusion pumps, pressure bag).
- Secure catheter and tubing. Apply dressing and wrist band.
- Frequently monitor IO site for extravasation of fluid.
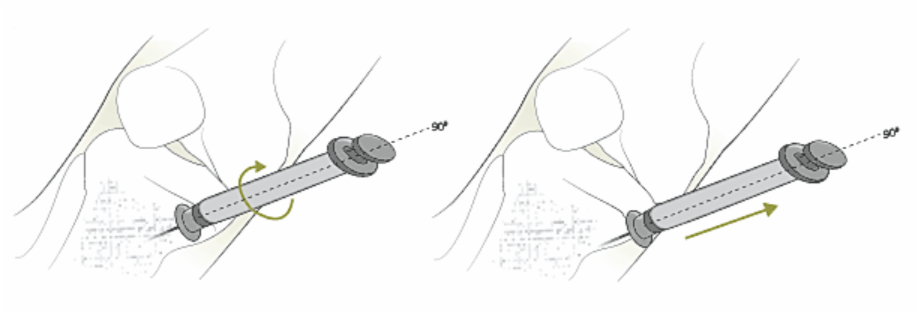
- IO catheter MUST be removed within 24 hours. Attach luer lock syringe and continuously and gently rotate clockwise while applying traction. Don’t ROCK or BEND the catheter during removal.
Caution: stylet and catheters are not MRI compatible.